One of the most common methods of producing identical parts in large quantities is the use of injection moulding. It’s often found in mass production environments, allowing thousands or millions of parts to be turned out quickly and reliably. A variety of materials can be injection moulded, but it’s mostly used for plastic.
Image Credit
Advantages of Injection Moulding
There are a number of advantages to injection moulding. The principal one is that once the initial set-up costs are covered it is easy to scale up production to a much larger level. This also means that the manufacturing cost per unit is lower the more you produce. The process also means there is very little variation in the parts produced, which is ideal where large volumes of identical components are needed.
Unlike other processes like machining, injection moulding creates much lower levels of waste material. Most of the waste comes from the ‘sprue’ – this is the part formed by the channels that guide the molten plastic into the mould. If you ever built Airfix kits as a kid, the sprue is the bit you throw away afterwards.
Of course, in plastic injection moulding carried out by a specialist like http://www.meadex.co.uk, depending on the material used the plastic in the sprue can be recycled, thus further cutting waste. This can even be done on the production line, adding the material back into the process.
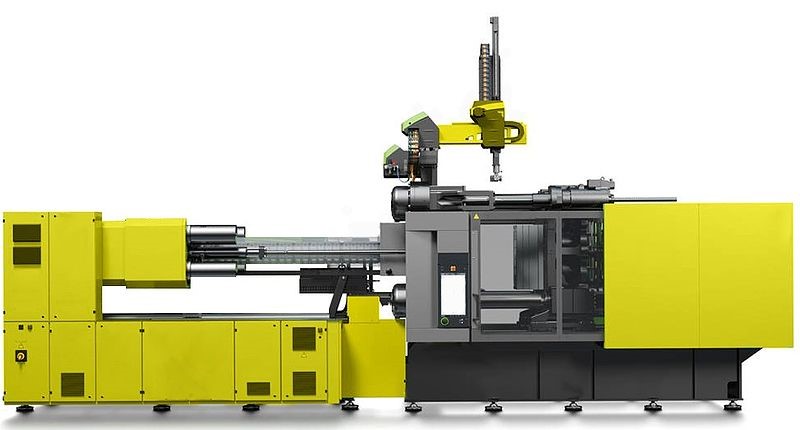

Image Credit
Drawbacks of Injection Moulding
There are of course some downsides to the process. The initial set-up of tooling is relatively expensive, so it’s important to get the design correct at the start and refine all the details before beginning large-scale production. Often today 3D printing is used to produce prototypes that can form the basis of a moulded part. Even so, you need to take account of the lead time required to begin producing a new product.
Once the moulds are made, making changes can be difficult and expensive, so again it’s important to get the design right at the start.
There are also restrictions on the size of components that can be produced due to the limitations of the machinery. This means that larger objects may need to me manufactured in several pieces and assembled afterwards. However, this restriction is equally true of other technologies, such as milling or 3D printing.

